Build a Zynthian
1 How to build a Zynthian (Prototype-3)
Manual is currently in development! (20150406)
1.1 Disclaimer
No guarantee for nothing. You do everything on your own risk!
1.2 Prerequisites
Want to join the Zynthian community? No problem! Building your own Zynthian is not very difficult. If you get trouble you can contact us at support@zynthian.org or via the blog http://blog.zynthian.org.
1.2.1 Required competences
For building the hardware you should have the following competences:
- Soldering
- Basic understanding of reading electronic circuit diagrams
- Enjoyment of work with electronic hardware and parts
1.2.2 Tools
- Screw drivers
- Soldering iron
- Tin-solder
- Side cutter
- Magnifiying glass
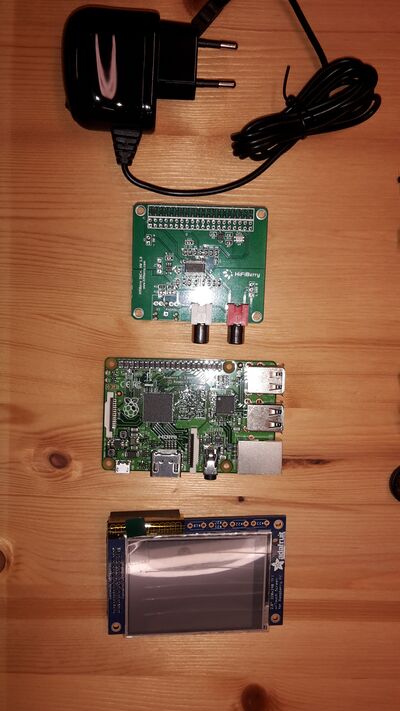
1.3 Hardware
1.3.1 Bill of Material
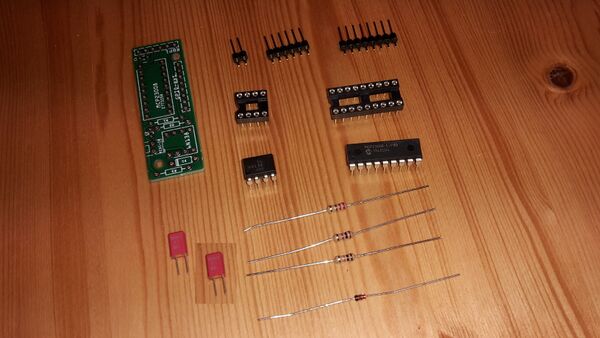
Here is a list of the hardware components you will need to build the Zynthian device. I also provided links to my suppliers and the prices I paid for the components in February 2016. I bought everything from Germany, so all descriptions are in German and prices are in EUR. If you live in another country maybe you'll get things even cheaper.
| No | Shipper | Order no. | Description | Pieces | Price per piece [€] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | http://www.reichelt.de | 1N 4148 | Planar Epitaxial Schaltdiode, DO35, 100V, 0,15A | 1 | 0,04 |
| 2 | http://www.reichelt.de | 6N 138 | OPTOKOPPLER | 1 | 0,58 |
| 3 | http://www.reichelt.de | RASPBERRY PI 2 | Raspberry Pi 2, 4x 900 MHz, 1 GB RAM | 1 | 37,50 |
| 4 | http://www.reichelt.de | RPI HB DAC+ RCA | HiFiBerry DAC+ RCA, Raspberry Pi Shield | 1 | 35,90 |
| 5 | http://www.reichelt.de | 1/4W 220 | Kohleschichtwiderstand 1/4W, 5%, 220 Ohm | 1 | 0,10 |
| 6 | http://www.reichelt.de | 1/4W 1,0K | Kohleschichtwiderstand 1/4W, 5%, 1,0 K-Ohm | 1 | 0,10 |
| 7 | http://www.reichelt.de | 1/4W 10K | Kohleschichtwiderstand 1/4W, 5%, 10 K-Ohm | 1 | 0,10 |
| 8 | http://www.reichelt.de | MKS-02 100N | WIMA Folienkondensator, Rm 2,5mm 100nF | 4 | 0,15 |
| 9 | http://www.reichelt.de | GS 18P | IC-Sockel, 18-polig, superflach, gedreht, vergold. | 1 | 0,32 |
| 10 | http://www.reichelt.de | GS 8P | IC-Sockel, 8-polig, superflach, gedreht, vergold. | 1 | 0,19 |
| 11 | http://www.reichelt.de | SL 2X25G 2,54 | 2x25pol.-Stiftleiste, gerade, RM 2,54 | 1 | 0,24 |
| 12 | http://www.reichelt.de | MAB 5S | DIN-Buchse, 5-polig | 1 | 0,24 |
| 13 (OPTIONAL) | http://www.reichelt.de | NTA 176 | 6,3 Mono-Klinken-Bu. auf Cinch-St. | 2 | 0,35 |
| 14 | http://www.reichelt.de | NT MUSB 2 SW | Micro-USB Steckernetzteil, schwarz, 5 V, 2 A | 1 | 8,40 |
| 15 | http://www.segor.de | MCP23008-E/P | MCP23008 8 port I2C-GPIO extender | 1 | 2,10 |
| 16 | http://www.amazon.de | Adafruit PiTFT 2.8" | Adafruit PiTFT Touchscreen Display, 2,8 Zoll, für Raspberry Pi Computer | 1 | 32,00 |
| 17 | http://www.ebay.de | 12mm Rotary Encoder Switch | Rotary Encoder with switch, 20 steps | 4 | 0,60 |
| 18 | http://www.ebay.de | Poti knob | Poti knob for Rotary encoder (Pos. 17) | 4 | 1,50 |
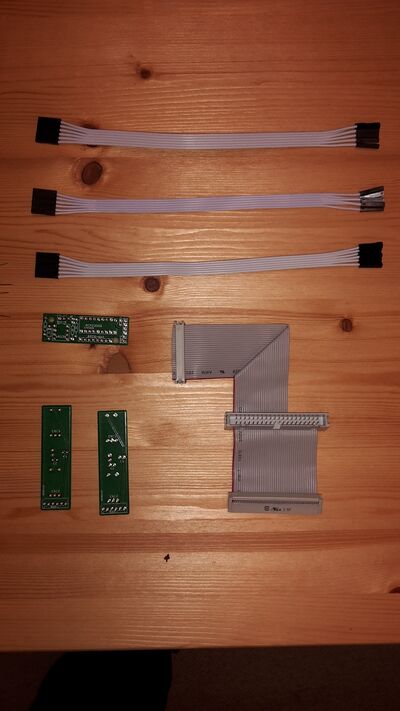
| 19 | http://blog.zynthian.org | Encoder PCB | PCB for encoders | 2 | 10,00 |
| 20 | http://blog.zynthian.org | 2in1 PCB | PCB for MIDI and GPIO extension | 1 | 10,00 |
| 21 | http://blog.zynthian.org | Main Bus Ribbon Cable | Raspberry Main Bus Ribbon Cable | 1 | 20,00 |
| 22 | http://blog.zynthian.org | Mini-ribbon cable | Mini-ribbon cable (6 pin female connector to 6 female jumper connectors | 3 | 3,00 |
| 23 | http://www.saturn.de | SD card | Samsung 32GB SD card | 1 | 14,00 |
| 24 | - | Short connector cables | Connector cables pin-female/pin-female for MIDI and external GPIO connector from 2in1 board | 4 | ??,?? |
| 25 | - | Multi-pin connector | 1x40pol.-Stiftleiste, gerade, RM 2,54 | 1 | ??,?? |
Notes:
- Pos. 19-22 were ordered directly from Zynthian.
- There is no case in this BoM - You have to build your own.
- Total price was 200,27 € (plus shipping).
1.4 Assembly and Soldering of the PCBs
1.4.1 Step 1: 2in1 board
1.4.1.1 You need:
- 1 * 2in1 PCB (Pos. 20)
- 2 * 100nF capacitor (Pos. 8)
- 1 * multi-pin 2 pins wide (part of pos. 24)
- 1 * multi-pin 6 pins wide (part of pos. 24)
- 1 * multi-pin 8 pins wide (part of pos. 24)
- 1 * resistor 10 kOhm (brown-black-orange-gold, pos. 7)
- 1 * resistor 1 kOhm (brown-black-red-gold, pos. 6)
- 1 * resistor 220 Ohm (red-red-black-gold, pos. 5)
- 1 * diode 1N4148 (pos. 1)
- 1 * IC socket 8 pins (pos. 10)
- 1 * IC socket 18 pins (pos. 9)
- 1 * IC 6N138 (pos. 2)
- 1 * IC MCP23008 (pos. 15)
- 2 * Connector cable pin-female/pin-female
- 1 * MIDI socket (DIN socket 5 pins)
- 1 * 2in1 PCB (pos. 20)
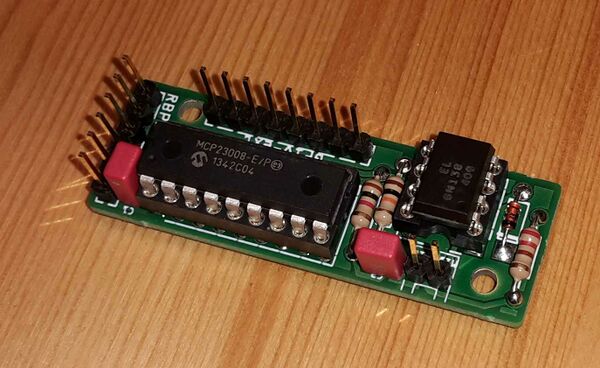
1.4.1.2 HowTo:
- Start with assembling the diode onto the PCB. Be careful to do this the right way - the small black (or white) stripe on one side of the diode must fit the same side of the white stripe on the PCB!
- After that solder the resistors.
- Then assemble the IC sockets, but do not fit the ICs yet. We will do this at the end of this task.
- After that, solder the capacitors and the multi-pin-rows.
- Now insert the ICs into the socket. Be careful to put them with the notch on the IC towards the hole of the white rectangle showing on the PCB!
For the MIDI socket you have to cut off one side of the female/female cable and solder this side to the DIN-socket. Connect the cables to pin 5 (2nd from left) and pin 4 (2nd from right).
1.4.2 Step 2: Encoder boards
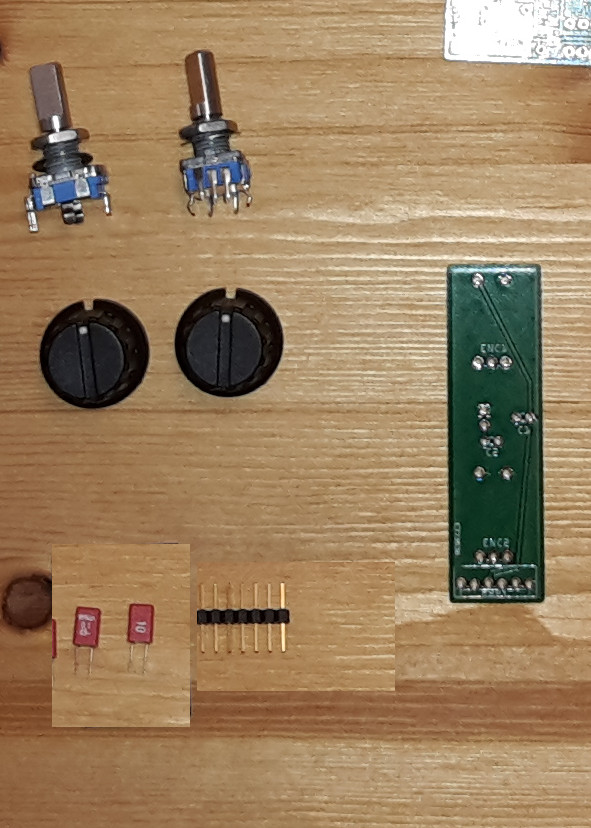
1.4.2.1 You need (for one Encoder PCB:
- 2 * Rotary Encoder with switch (Pos. 17)
- 2 * 100nF capacitor (Pos. 8)
- 1 * multi-pin 6 pins wide (part of Pos. 24)
- 1 * multi-pin 2 pins wide (part of Pos. 24)
- 1 * Encoder PCB (Pos. 19)
1.4.2.2 HowTo:
- Notice! Due to the mounting of the encoders on a front panel, the 6-pin-row must be soldered from the bottom of the PCB (pin numbering will be 1..6 from the lower side of the PCB!). The picture below shows the WRONG component side! (newer images will follow)
- The order of the following steps is not important: Solder the capacitors, the 2-pin-rows and the Encoders on the board (on the upper side) - that's it.
- You have to do this twice - you need two encoder boards.
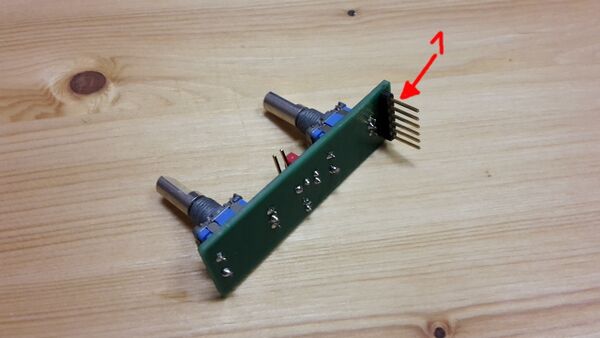
Alternative: Mount the pin row at the bottom of the PCB:
1.4.3 Step 3: Pin row on the Hifiberry
1.4.3.1 You need:
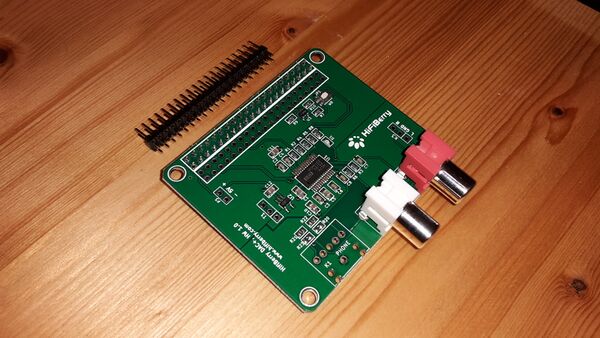
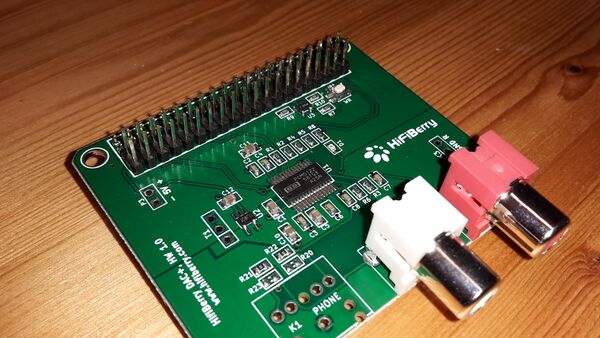
- 1 * HiFiBerry DAC+ RCA, Raspberry Pi Shield (Pos. 4)
- 1 * 2x25pol.-Stiftleiste, gerade, RM 2,54 (Pos. 11)
1.4.3.2 HowTo:
- For this part you should have some time. It will be very worse when damaging the Hifiberry!
- First of all: cut the 2*25 pin-row to 2*20 pin (perhaps with a cutter).
- Place the pin-row on the Hifiberry and start to solder on the back of the Hifiberry. I used to solder pins which are not next together to avoid hot spots. You also can pause some time for cooling down the area you soldered last.
1.4.4 Checking everything
Congratulations - half the way done!
Now you should double-check everything you soldered:
- Were the components soldered in their correct orientation (e.g. polarity, pin layout)?
- Are there any solder bridges between pins? Remove them!
- Is the diode on the 2in1-PCB correctly oriented?
- Are the ICs showing the right direction?
- Are all pins of the ICs in their socket?
Hints:
- Use the magnifying glass and bright light for checking.
1.5 Connecting the cables
1.5.1 You need:
- 1 * Raspberry Pi 2 (Pos. 3)
- 1 * HiFiBerry DAC+ RCA (Pos. 4)
- 1 * Adafruit PiTFT Touchscreen Display, 2,8 Zoll (Pos. 16)
- 1 * Raspberry Main Bus Ribbon Cable (Pos. 21)
- 3 * Mini-ribbon cable (6 pin female connector to 6 female jumper connectors(Pos. 22)
- 2 * Connector cables pin-female/pin-female (Pos. 24)
1.5.2 Raspberry Pi and Hifiberry DAC+
Put the Hifiberry DAC+ onto the Raspberry Pi. With the Hifiberry there come 4 distance pieces and 4 screws (all plastic). Put them together as shown in the following picture.
1.5.3 TFT
Time for connecting thesuitable main-ribbon-cable with the (female) 40-pin-connector onto the Hifiberry. At the end of the cable is a (female) 26-pin-connector. This one must be connected onto the PiTFT. If you have a clone PiTFT which has no suitable port you have to solder one or use a gender changer. The original PiTFT has both versions of connector.
1.5.4 2in1
The 2in1-PCB must be connected using one of the mini-ribbon cables. The 6-pin connector must be located towards the PCB. Pin 1 is on the left bottom (component side up). On the other end of the cable are 1-pin female connectors. They must be connected onto the following pins on the (male) 40-pin-conenctor in the middle of the main-ribbon cable.
| Wire no. | Function | GPIO no. | Pin on Raspi no. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vdc 3.3V | 3.3V | 1 |
| 2 | RxD | RxD | 10 |
| 3 | I2C SDA1 | 09 | 5 |
| 4 | I2C SCL1 | 08 | 3 |
| 5 | Vdc 5V | %v | 2/4 |
| 6 | GND | GND | 6/9 |
Next connect the DIN socket (MIDI) onto the 2in1-PCB. The connector on the PCB is the 2-pin one located on the upper right of the PCB.
| Wire no. | Function | MIDI-IN pin no. |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | MIDI-IN-5 | 5 (MIDI connector: 2nd from left) |
| 2 | RxD | 4 (MIDI connector: 2nd from right) |
1.5.5 Controller
This is a little bit tricky. Depending on you setup it maybe useful to put the 6-pin-row on the back of the PCB. So you can front mount the encoders. I haven't done this: I used to bend the 6-pin-row by 90 degree. The original Zynthian does this not - so the pin counting is changed!
Looking on the top of the PCB with the 6-pin-row down:
- Mounting the 6-pin-row on top of the PCB: Pin counting starts on the left of the row!
- Mounting the 6-pin-row on the back of the PCB: Pin counting starts on the right of the row!
There some encoders that has reversed the pin order, so you have to change A and B pins.
1.5.5.1 Controller 1
| Wire no. | Function | GPIO no. | Pin on Raspi no. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Enc1-B | 25 | 37 |
| 2 | ENC1-A | 27 | 36 |
| 3 | Enc1-SW | 23 | 33 |
| 4 | Enc2-B | 26 | 32 |
| 5 | Enc2-A | 21 | 29 |
| 6 | GND | GND | 30 |
| Wire no. | Function | Pin on 2in1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | - |
| 2 | Enc2-SW | X07 |
1.5.5.2 Controller 2
| Wire no. | Function | GPIO no. | Pin on Raspi no. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Enc1-B | 04 | 16 |
| 2 | ENC1-A | 03 | 15 |
| 3 | Enc1-SW | 02 | 13 |
| 4 | Enc2-B | 00 | 11 |
| 5 | Enc2-A | 07 | 07 |
| 6 | GND | GND | 14 |
| Wire no. | Function | Pin on 2in1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | - |
| 2 | Enc2-SW | X08 |
1.6 Creating the SD
1.6.1 Getting the Image
Currently the image is only available via torrent:
Download torrent link (sha1sum: 848598e5d4aa4a432a9c0cb7fe1ea120b037eac2)
1.6.2 Writing the image to the SD card
If you got the whole image you can write it to an SD-card. Depending on your OS you have to choose how to create the SD-card. You need a minimum size of 16GB, better 32GB for more sample-sets in future. There is a really good manual for this at | https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/installation/installing-images/.