Difference between revisions of "Adding Extra I/O with the Zynaptik Module"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | |||
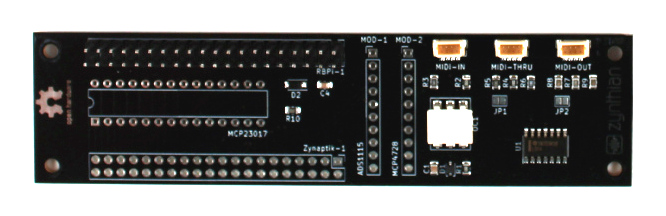
| + | The Zynaptik module allows to solder on it 3 extra submodules and a 40 pin header for interfacing them: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Zynaptik_top.jpg|900px]] | ||
| + | |||
[[File:Zynaptik_40pin_header.png|300px|right]] | [[File:Zynaptik_40pin_header.png|300px|right]] | ||
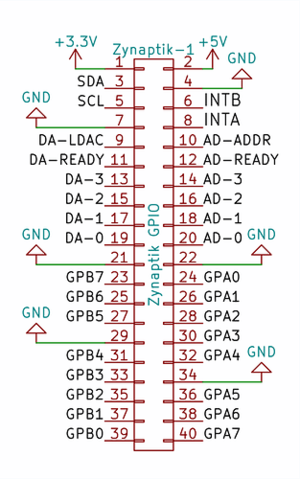
| + | '''+ Secondary MCP23017 (Digital I/O):''' It uses I2C address 0x21 and the 2 interrupt lines are connected to the RBPi GPIO. INTA to GPIO27 (pin 36) and INTB to GPIO25 (pin 37). The digital I/O are labelled as GPAx & GPBx on the Zynaptik's header schematic. | ||
| − | + | Currently you can use it for adding more switches (yet!) to your zynthian. There are plans for integrating the HC-SR04 (Ultrasonic Distance Sensor) and using it for controlling parameters (MIDI-CC). Would you like to be the first one having a Therezyn? | |
| − | |||
| − | Currently you can use it for adding more switches (yet!) to your zynthian. There are plans for integrating the HC-SR04 (Ultrasonic Distance Sensor) and using it for controlling parameters (MIDI-CC). Would you like to be the first having a Therezyn? | ||
| − | '''ADS1115 (Analog Input):''' It uses I2C address 0x48. The 4 analog input pins are labelled as ADx on the Zynaptik's header schematic. | + | '''+ ADS1115 (MOD-1 Analog Input):''' It uses I2C address 0x48 by default. The 4 analog input pins are labelled as ADx on the Zynaptik's header schematic. |
The Zynaptik library currently implements a mechanism for assigning the Analog Inputs to MIDI-CC. This can be used for connecting CV-IN or for controlling sound engine parameters using analog sensors. | The Zynaptik library currently implements a mechanism for assigning the Analog Inputs to MIDI-CC. This can be used for connecting CV-IN or for controlling sound engine parameters using analog sensors. | ||
| − | '''MCP4728 (Analog Output):''' It uses I2C address 0x60. The 4 analog output pins are labelled as DAx on the Zynaptik's header schematic. | + | '''+ MCP4728 (MOD-2 Analog Output):''' It uses I2C address 0x60 by default. The 4 analog output pins are labelled as DAx on the Zynaptik's header schematic. |
It's currently unimplemented in Zynaptik library. Would you like to do it? The highest honor is deserved to the brave who kill this dragon ... | It's currently unimplemented in Zynaptik library. Would you like to do it? The highest honor is deserved to the brave who kill this dragon ... | ||
Revision as of 23:01, 16 August 2020
The Zynaptik module allows to solder on it 3 extra submodules and a 40 pin header for interfacing them:
+ Secondary MCP23017 (Digital I/O): It uses I2C address 0x21 and the 2 interrupt lines are connected to the RBPi GPIO. INTA to GPIO27 (pin 36) and INTB to GPIO25 (pin 37). The digital I/O are labelled as GPAx & GPBx on the Zynaptik's header schematic.
Currently you can use it for adding more switches (yet!) to your zynthian. There are plans for integrating the HC-SR04 (Ultrasonic Distance Sensor) and using it for controlling parameters (MIDI-CC). Would you like to be the first one having a Therezyn?
+ ADS1115 (MOD-1 Analog Input): It uses I2C address 0x48 by default. The 4 analog input pins are labelled as ADx on the Zynaptik's header schematic.
The Zynaptik library currently implements a mechanism for assigning the Analog Inputs to MIDI-CC. This can be used for connecting CV-IN or for controlling sound engine parameters using analog sensors.
+ MCP4728 (MOD-2 Analog Output): It uses I2C address 0x60 by default. The 4 analog output pins are labelled as DAx on the Zynaptik's header schematic.
It's currently unimplemented in Zynaptik library. Would you like to do it? The highest honor is deserved to the brave who kill this dragon ...